The Chemical Composition of Hair: A Comprehensive Guide for Cosmetologists and Haircare Experts
The field of cosmetology goes beyond cutting, styling, and coloring hair; it involves a deep understanding of the science behind hair growth and composition. One of the foundational aspects of this knowledge is the chemical composition of hair. This article aims to shed light on this essential topic, from the structure of hair at the cellular level to the molecules that give it its unique properties.

Hair
The Basics: Keratin and Keratinization
Hair is principally composed of keratin, a protein also found in skin and nails. Keratinization is the process by which living cells from the hair bulb mature, die, and become a part of the hair strand. The process encompasses:
- Cell Maturation: New cells form and fill up with keratin.
- Nucleus Loss: As these cells move upward, they lose their nucleus and die.
- Keratinization: Once the hair strand is visible above the scalp, the cells are dead and fully keratinized.
The Chemical Building Blocks of Hair
Protein Constituents
- Keratin: Makes up about 90% of the hair. It provides hair with its basic structure and strength.
Minor Components
- Water: Essential for maintaining the elasticity of hair.
- Lipids: Contribute to the hair’s sheen and texture.
- Trace Minerals: Present in minute quantities but play a role in hair’s overall health and color.
The COHNS Elements
The major elements found in hair are Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur (COHNS). These elements are vital not just for hair but also for skin and nails.
The COHNS Elements | |
Element | % in Avg. Hair |
Carbon | 51 |
Oxygen | 21 |
Hydrogen | 6 |
Nitrogen | 17 |
Sulfur | 5 |
The COHNS Elements
Amino Acids and Peptide Bonds
Amino acids are the smallest units that form the keratin protein. These amino acids are linked together by very strong chemical bonds known as peptide bonds or end bonds. Once linked, they form a long chain called a polypeptide chain. These chains adopt a spiral structure called a helix.
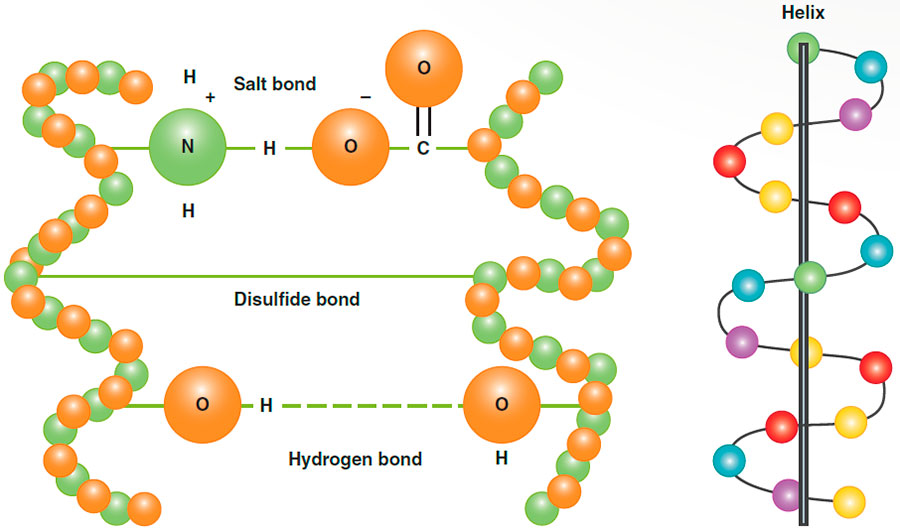
Relevance in Cosmetology
- Chemical Treatments: Understanding hair composition is crucial for successful chemical treatments like perms, relaxers, or hair coloring. Knowing how keratinization works can help you predict how hair will respond to these treatments.
- Hair Damage Repair: Identifying the loss of essential components like lipids or proteins can help in recommending targeted treatments.
- Personalized Haircare: Each individual’s hair has unique chemical attributes. A thorough understanding helps in crafting personalized haircare regimens.
- Product Development: The information is also useful in the development and refinement of hair care products, ensuring they address the specific needs of different hair types.
- Consultation Skills: A well-informed cosmetologist can offer insightful consultations, educating clients on their hair’s needs based on its chemical composition.
Conclusion
The chemical composition of hair is an intricate subject, but one that is essential for every serious cosmetologist. Understanding the role of each chemical component, from proteins to amino acids, provides a deeper comprehension of how hair grows, reacts to treatments, and ultimately, how it can be maintained in a healthy state. Such understanding doesn’t just make you a better cosmetologist; it offers the possibility for true expertise in the field. With this knowledge, cosmetologists can offer services that are scientifically informed, ultimately leading to better outcomes for their clients.






