Understanding Hair Shaft Structure: An In-Depth Guide for Beauticians and Hair Care Professionals

Hair Shaft Structure
In the beauty industry, an intimate understanding of hair structure is paramount for delivering effective and tailored services. While many professionals focus on the hair root, an equal amount of attention must be given to the hair shaft. Knowledge of its intricate composition can dramatically impact the results of hairstyling, chemical treatments, and even basic hair care. This article delves into the structure of the hair shaft and its relevance in the field of cosmetology.
Anatomy of the Hair Shaft: Cuticle, Cortex, and Medulla
A single strand of hair isn’t as simple as it seems. The hair shaft, which is the portion of hair visible above the scalp, consists of three main layers: the cuticle, cortex, and, sometimes, the medulla.
The Cuticle: The Hair’s Protective Shield
- Structure: The outermost layer of the hair shaft, the cuticle, is made up of overlapping cells resembling roof shingles.
- Function: The cuticle serves as a protective barrier for the cortex. In healthy hair, the cuticle layers lie flat, providing a sheen and also preventing moisture loss.
- Reactivity: During chemical treatments, the cuticle softens and swells, allowing the chemicals to infiltrate the cortex. Therefore, the integrity of the cuticle is crucial for how hair responds to chemical services.
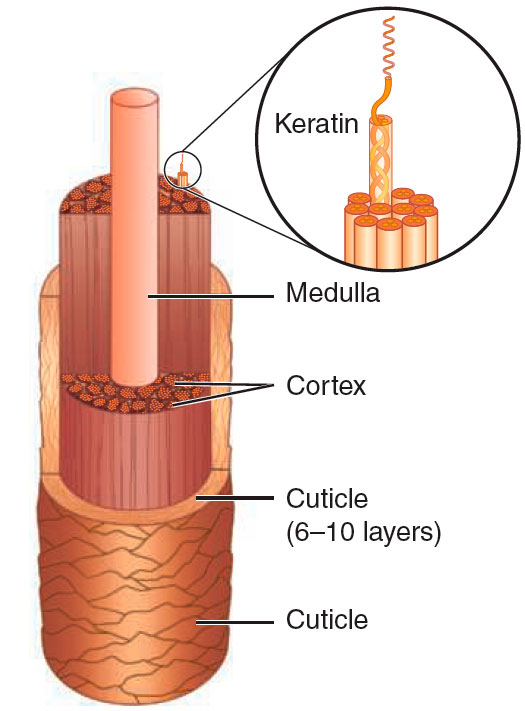
The Cortex: The Hair’s Backbone
- Structure: Beneath the cuticle is the cortex, composed of fibrous proteins.
- Function: Accounting for about 90% of the hair’s weight, the cortex determines the hair’s strength, elasticity, and color.
- Reactivity: The cortex is the primary target for most chemical hair treatments, such as coloring and perming. Its health dictates how well the hair withstands these processes.
The Medulla: The Optional Core
- Structure: Known as the hair’s pith or core, the medulla is not present in all hair types.
- Variability: Generally, coarse and beard hair contains a medulla, while fine hair usually does not.
- Function: The medulla’s role is not entirely understood but it does not seem to have a significant effect on hair’s tensile strength or cosmetic appearance.
The Importance in Beautician Work
- Chemical Treatments: Knowing the shaft structure helps beauticians accurately gauge how hair will react to chemical treatments. For instance, a healthy cuticle will be more resilient to chemical damage.
- Styling and Texturing: Understanding the cortex’s role allows beauticians to utilize techniques that can alter the hair’s texture and style without causing damage.
- Client Consultation: Detailed knowledge allows for transparent and effective communication with clients. A beautician can explain why a particular treatment may or may not be suitable based on the hair shaft’s condition.
- Product Recommendations: Hair care products often target specific layers of the hair shaft. Professional advice can therefore be more tailored and effective.
- Treatment of Damaged Hair: In cases of damaged cuticle or weakened cortex, a beautician with a thorough understanding of the hair shaft can recommend treatments to rebuild and protect these layers.
- Personalization: Hair types differ in whether or not they possess a medulla, and this can influence the choice of treatment protocols.
Conclusion
The hair shaft is a complex structure with layers that have distinct properties and functions. For beauticians, an in-depth understanding of these layers is not just academic—it has practical applications that can significantly impact the quality of service offered to clients. By leveraging this knowledge, hair care professionals can provide services that are both effective and personalized, leading to better client satisfaction and, ultimately, healthier, more beautiful hair.






