Mapping the Head: A Hairdresser’s Guide to Anatomy and Precision
In the realm of hairdressing, understanding the intricate layout of the head is paramount. Each section of the head has its unique characteristics that influence both the cutting and styling process. This comprehensive guide offers an in-depth examination of the areas of the head, elucidating how a hairdresser can employ this knowledge to perfect their craft.
1. The Top of the Head: Gravity’s Playground
Characteristics and Identification: The top area, located via the parietal ridge, comprises the hair that grows atop the head, lying directly on its shape. Hair below the parietal ridge or crest experiences the pull of gravity, causing it to hang. Identifying this zone is done by parting the hair at the parietal ridge and following the curve around the head.
Hairdressing Insights: As the top hair directly rests on the skull, it provides volume and lift. Techniques such as layering or texturizing are often employed here to add dimension.
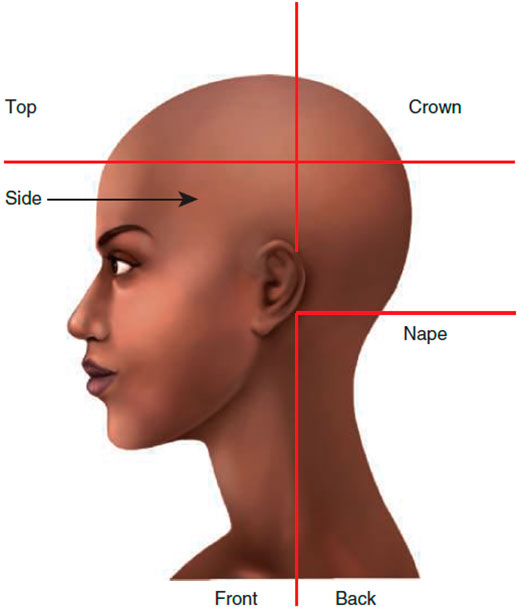
2. The Frontal Mystery
Characteristics and Identification: To determine the front area, draw a line from the apex to the ear’s back. Hair that naturally cascades in front of the ear denotes this region.
Hairdressing Insights: The front often sets the stage for the face, influencing face-framing layers, bangs, or side-swept looks.
3. Sides: The Contour Specialists
Characteristics: The sides encompass all the hair below the parietal ridge from the ear’s back and forward.
Hairdressing Insights: This area plays a pivotal role in contouring the face. Techniques such as graduation can enhance facial features or even camouflage flaws.
4. The Crown: The Challenging Curve
Characteristics: The region between the apex and the parietal ridge’s back is termed the crown. This area can be tricky, as many individuals possess flat crowns with cowlicks or whorls.
Hairdressing Insights: Given its unique growth patterns, precise layering and directionality during styling are crucial for the crown area.
5. The Nape: Grace at the Back
Characteristics and Identification: Located as the rear part of the neck, the nape consists of the hair beneath the occipital bone. Identifying it involves drawing a line across the head’s back at the occipital bone.
Hairdressing Insights: The nape offers a canvas for undercuts, intricate designs, or tapered finishes, especially in shorter hairstyles.
6. The Back: The Vast Expanse
Characteristics and Identification: By drawing a line from the apex towards the ear’s back, one can define the back. This section houses all the hair that falls naturally behind the ear.
Hairdressing Insights: As a substantial area, the back influences the overall volume and length. Techniques such as stacking or V-cut can be implemented here for visual appeal.
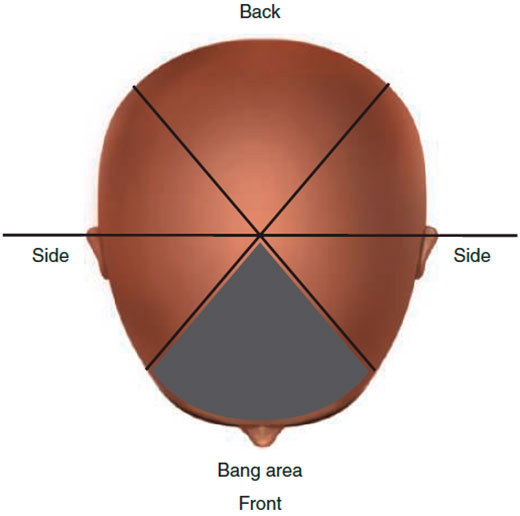
7. The Bang or Fringe Area: The Face’s Frame
Characteristics and Identification: This triangular section starts at the apex and concludes at the front corners. The area begins where a comb, balanced on the apex, leaves the head. The bang area should not fall beyond the outer corners of the eyes when in its natural position.
Hairdressing Insights: From curtain bangs to side fringes, this zone is all about framing and accentuating facial features.
Conclusion
A head is not merely a canvas for a hairdresser; it’s a topographical wonder. Recognizing and respecting the anatomy of the head allows hairdressers to craft hair designs that don’t just look good but also harmonize with the client’s unique head structure. This synergy between anatomy and artistry is the hallmark of great hair design.






