The Crucial Role of Contrast Agents in Diagnostic Imaging
This article explores the pivotal function of contrast agents in diagnostic imaging procedures. It dives into the use of barium sulfate in gastrointestinal examinations and iodine-based molecules in visualizing vascular and urinary systems, discussing their specific applications and safety considerations. The piece underscores the significance of contrast agents in enhancing medical imaging and thus facilitating accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.

The Crucial Role of Contrast Agents in Diagnostic Imaging
Let’s discuss the use of contrast agents in diagnostic imaging with a focus on their purpose, types, and safety considerations.
Contrast agents play a pivotal role in diagnostic imaging, enhancing the differentiation of structures and tissues within the body, making certain areas more clearly visible on radiographs. They act by altering the way X-rays or other imaging tools interact with the body, highlighting specific areas or systems.
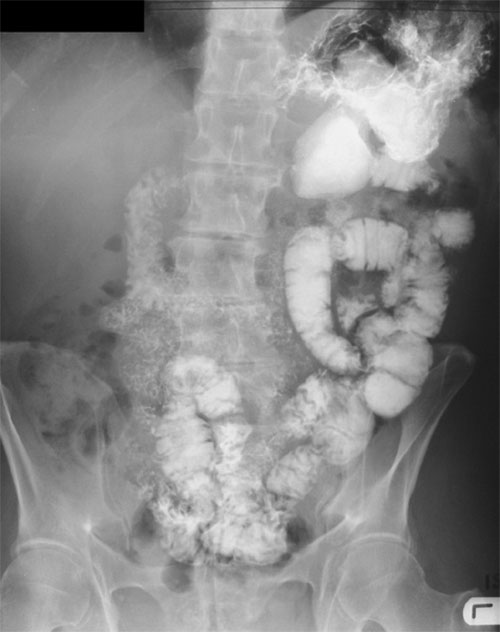
Barium sulfate is one such contrast agent used extensively in the examination of the gastrointestinal tract. As an insoluble salt, it doesn’t dissolve easily, enabling the lining of the esophagus, stomach, or intestines to be coated and appear more visibly on an X-ray film. This allows healthcare providers to observe the bowel lumen in detail and identify any anomalies. To improve the imaging quality, a technique called a double-contrast (air/barium) study is often used. This technique involves the addition of air to the barium sulfate suspension, enhancing the difference in radiographic density and providing a clearer, more detailed image.
When it comes to visualizing vascular structures like arteries and veins, iodine-based molecules serve as effective contrast agents. The high atomic mass of iodine ensures significant attenuation of X-rays, creating a stark contrast in images. Moreover, iodine is naturally excreted through the kidneys, minimizing the risk of accumulations in the body. These properties make iodine-based agents suitable for intravenous or intra-arterial injection. Nevertheless, safety precautions are crucial, as rare instances of anaphylactic reactions can occur.
In addition to aiding in the visualization of vascular structures, these contrast agents can also be employed in intravenous urography. This is a radiological procedure to examine the urinary system, including kidneys, ureters, and bladder, providing valuable information about their structure and function.
In conclusion, contrast agents like barium sulfate and iodine-based molecules are integral to the field of diagnostic imaging, aiding physicians in identifying, diagnosing, and treating a wide array of health conditions.











