Understanding the Nervous System: Structure and Function
The nervous system is a complex and intricate network of specialized cells and structures that facilitate communication and coordination throughout the body. It plays a crucial role in controlling various bodily functions and orchestrating responses to internal and external stimuli. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the structure and function of the nervous system, highlighting its divisions, including the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), as well as its somatic and visceral components.
Nervous System
I. Structural Divisions of the Nervous System: The nervous system can be divided structurally into two main components:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. These vital structures develop from the neural tube during embryonic development. The brain serves as the command center, responsible for processing and integrating sensory information, initiating motor responses, and regulating higher cognitive functions. The spinal cord, an elongated bundle of nerve fibers, connects the brain to the rest of the body and serves as a pathway for transmitting signals between the brain and peripheral nerves.
-
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): The PNS encompasses all nervous structures outside the CNS that connect it to the body. Elements of the PNS develop from neural crest cells and as outgrowths of the CNS. It includes various components:
a. Spinal and Cranial Nerves: The PNS comprises a network of spinal and cranial nerves that extend from the spinal cord and brain, respectively. These nerves transmit sensory information from the body to the CNS and carry motor signals from the CNS to muscles and glands, facilitating movement and bodily functions.
b. Visceral Nerves and Plexuses: Visceral nerves innervate organs and glands within the body, regulating autonomic functions such as digestion, respiration, and cardiovascular activity. Plexuses, intricate networks of nerves, are found in various regions of the body and play a crucial role in integrating and distributing nerve signals to specific target organs.
c. Enteric System: The enteric system, often referred to as the “second brain,” consists of a complex network of neurons located within the walls of the digestive tract. It regulates gastrointestinal functions independently of the CNS, controlling processes such as digestion, nutrient absorption, and gut motility.
II. Functional Divisions of the Nervous System: In addition to its structural divisions, the nervous system can also be classified based on its functional components:
- Somatic Nervous System: The somatic nervous system governs voluntary movements and sensory perception. It controls skeletal muscles and relays sensory information from the body’s external environment to the CNS, enabling conscious awareness of touch, temperature, pain, and other sensations.
- Visceral Nervous System: The visceral nervous system, also known as the autonomic nervous system, regulates involuntary bodily functions, including those of internal organs and glands. It operates largely outside conscious control and is further divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, which exert opposing effects to maintain homeostasis.
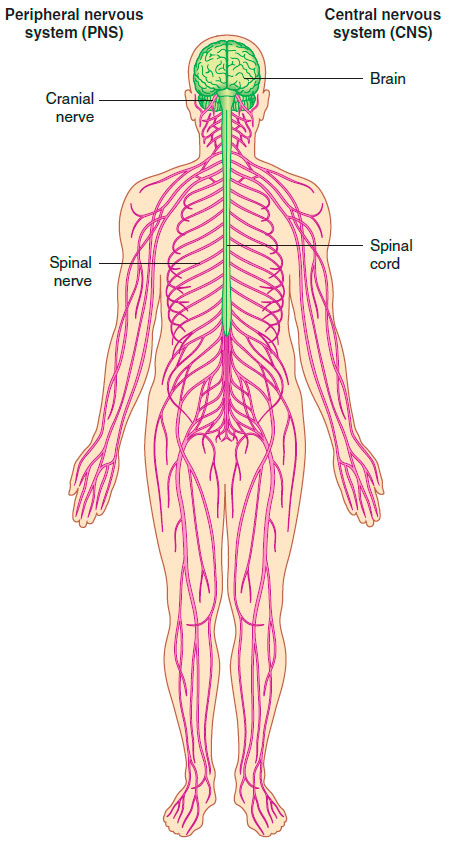
The nervous system is a remarkable and intricate network responsible for coordinating and regulating bodily functions. Its structural divisions, including the CNS and PNS, ensure efficient communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. Moreover, its functional divisions, the somatic and visceral components, enable voluntary movements and regulate internal processes. Understanding the structure and function of the nervous system is vital in diagnosing and treating various neurological conditions, ultimately improving the overall well-being of individuals.












