The Pathways of the Body
The human body is a complex and interconnected system, with every part relying on the other to function properly. This vast network of communication is facilitated by nerves, whitish bundles of fibers that transmit impulses across the body. Originating from the brain and spinal cord, nerves extend to every corner of the body, sending and receiving messages crucial for our existence. Understanding the role and function of nerves offers insight into the various sensations we experience, from the gentlest touch to the harshest pain.
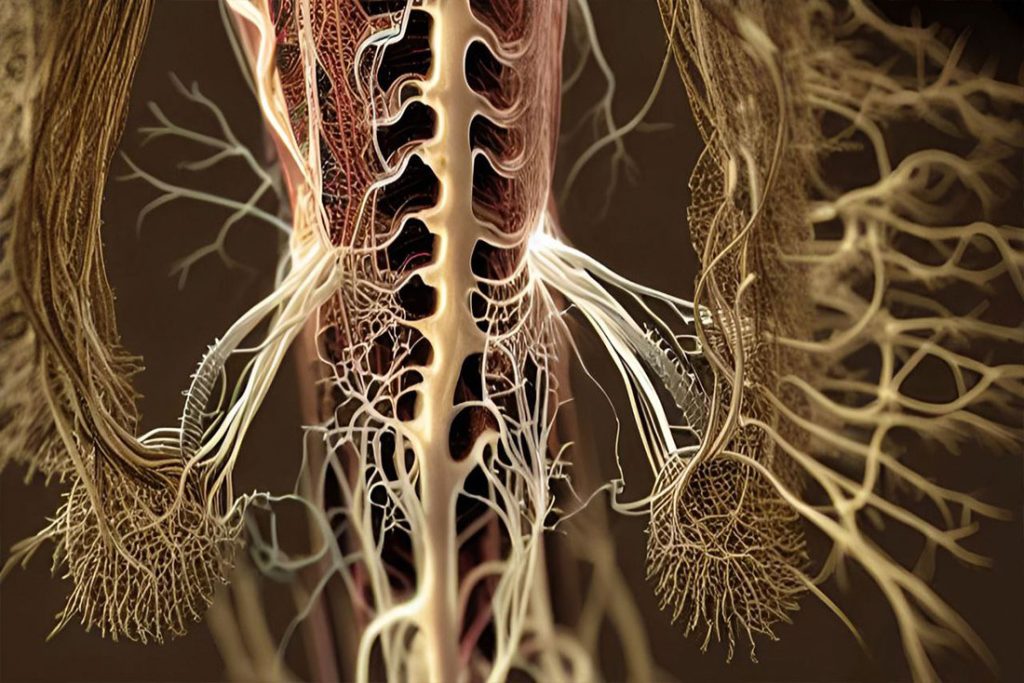
Nerves
The Nature of Nerves
Nerves, by their nature, are incredibly complex structures. Composed of bundles of axons, they are responsible for carrying electrical signals, also known as nerve impulses, between the brain and other body parts. Each nerve is encased in a protective sheath, which facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses and helps prevent damage to the nerve fibers themselves.
Nerves can be categorized into three major types: sensory nerves, motor nerves, and mixed nerves. Sensory nerves carry signals from sensory receptors in the skin, muscles, and other body parts to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), enabling us to perceive touch, temperature, pain, and other sensations. Motor nerves carry signals from the central nervous system to the muscles, glands, and other effector tissues, controlling their activity. Mixed nerves, as the name suggests, perform both functions.
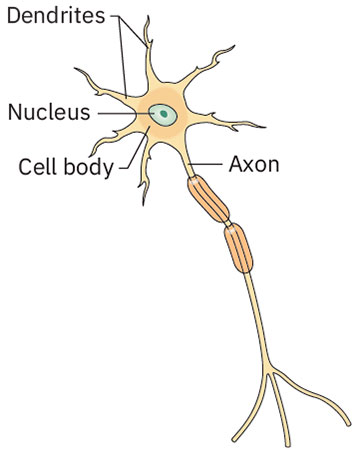
The Role of Nerves in Health and Disease
In the context of health and disease, nerves play an essential role. Their function is critical in detecting changes in the body’s internal and external environment and responding accordingly, whether by initiating movement, modulating organ function, or relaying sensory information to the brain for interpretation.
When nerves function as they should, we may scarcely notice their activity. However, when a nerve becomes damaged, the resulting dysfunction can manifest in a wide array of symptoms, depending on which nerve is affected. For example, damage to a motor nerve can lead to weakness or paralysis of the muscles it supplies, while damage to a sensory nerve can cause numbness, tingling, or pain.
In certain conditions, such as peripheral neuropathy, multiple nerves can be affected simultaneously, leading to symptoms in various parts of the body. Other diseases, like multiple sclerosis, primarily affect the nerves of the central nervous system, resulting in a different constellation of symptoms. Understanding the role of nerves in these conditions is vital for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management.
The nervous system, with its extensive network of nerves, is undeniably one of the body’s most fascinating and intricate systems. From their origination in the brain and spinal cord to their farthest reaches in the fingertips and toes, nerves facilitate an astonishing array of bodily functions. As research continues to unveil the mysteries of the nervous system, our understanding of how to maintain nerve health, treat nerve-related conditions, and enhance the body’s performance continues to grow. As such, the nerves hold a central position in our continued exploration of human health and disease.






