The Integumentary System: Essential Knowledge for Cosmetologists
As a cosmetologist, knowledge of the integumentary system—the body’s protective covering comprising the skin and its accessory organs—is integral. The skin, along with hair, nails, sweat glands, and oil glands, serves essential roles in protection, regulation, and sensation. Understanding its functions and structures allows cosmetologists to enhance their services while ensuring client safety.

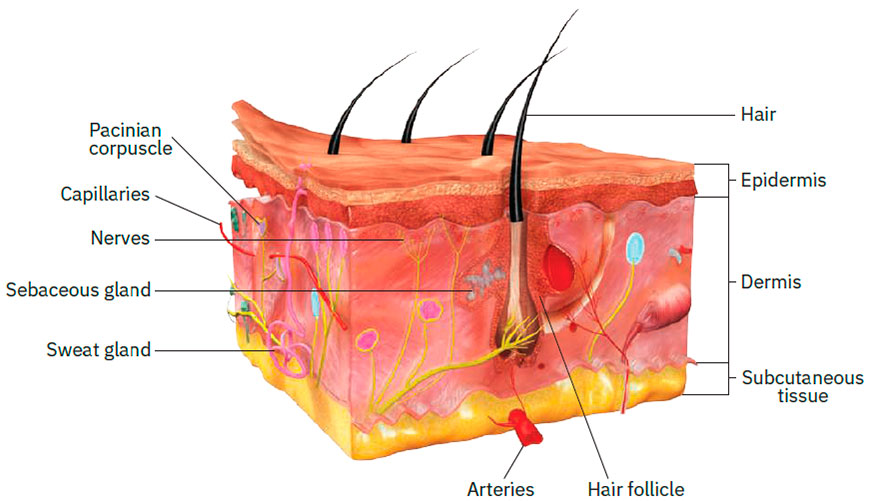
The Integumentary System
Understanding the Integumentary System
The integumentary system’s primary component, the skin, is the largest organ in the human body. It serves as the body’s primary line of defense against external aggressors, such as germs, harmful chemicals, and UV rays. It also regulates body temperature and is involved in sensory perception.
Accessories to the skin include:
- Hair: Provides a certain degree of thermal insulation and enhances the detection of things that lightly touch the skin.
- Nails: Protect the sensitive tips of fingers and toes and can be indicative of a person’s general health status.
- Sweat Glands: Help to regulate body temperature through evaporative cooling.
- Oil Glands: Secrete sebum, a substance that keeps skin and hair moisturized and helps create a barrier against harmful substances.
The Role of the Integumentary System in Cosmetology
Understanding the integumentary system can enable cosmetologists to deliver treatments more effectively. They can identify different skin types, conditions, and disorders, allowing them to recommend suitable treatments and products. For instance, a client with dry skin may benefit from treatments and products that boost hydration and improve sebum production.
The condition of a client’s skin, hair, or nails can also signal underlying health issues. Changes in the skin’s appearance, nail discolorations, or unusual hair loss could indicate health conditions requiring medical attention.
Safety Considerations for the Integumentary System
Awareness of the skin’s health and integrity is critical in cosmetology. Some conditions may contraindicate certain treatments. For example, inflamed, broken, or diseased skin should not be massaged, and certain chemical treatments could be detrimental to clients with specific skin disorders.
Knowledge of the integumentary system is invaluable to cosmetologists. It not only underpins their understanding of skin health and the effects of various treatments, but it also promotes safety, allowing them to recognize when services may be harmful or require adaptation. By honing their knowledge of the skin and its associated structures, cosmetologists can ensure they provide their clients with safe, effective, and personalized treatments.






