In-depth Exploration of Aging Skin Issues: The Roles of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors
Aging is an inevitable part of life, and our skin is no exception. As time progresses, the visual signs of skin aging, such as wrinkles, age spots, and changes in skin tone, become more apparent and can be a major concern for many. This article delves into the complex process of skin aging, focusing on the crucial roles that both intrinsic and extrinsic factors play. It also underscores how these factors affect not only our skin health but also our overall well-being.

Aging Skin
Understanding Intrinsic Factors of Skin Aging
Intrinsic aging is the natural, chronological aging process that largely depends on genetic factors. Regardless of outside influences, our skin will age due to the passage of time. There are several intrinsic factors at play:
Genetics and Ethnicity
Our genes are a fundamental aspect of how and when we age. They can dictate when we start to see fine lines or changes in skin elasticity, and the extent to which these signs of aging manifest. Different ethnicities, owing to their unique genetic makeup, may age differently. For example, those with darker skin often have more melanin, which can offer some protection against wrinkles and skin sagging.
Gravity
Gravity is a relentless force that impacts the skin by pulling it downward over time. As the skin’s elasticity decreases with age, the effects of gravity become more apparent, leading to drooping eyelids, elongated earlobes, and jowls.
Repetitive Facial Expressions
Repeated facial movements, such as smiling, frowning, or squinting, eventually lead to the formation of lines and wrinkles in the skin. This is due to the continuous contracting and relaxing of facial muscles, which over time can wear down the skin’s elasticity and cause permanent lines.
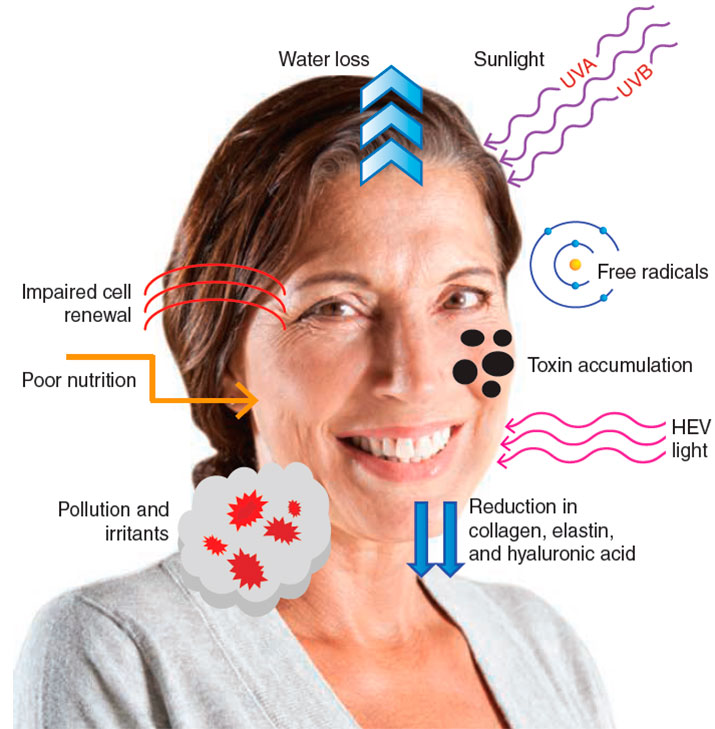
The Role of Extrinsic Factors in Skin Aging
Extrinsic aging refers to aging that occurs due to environmental and lifestyle factors. Unlike intrinsic aging, extrinsic aging can be largely controlled and its effects minimized. Let’s take a closer look at these factors:
UV Radiation
Exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation is one of the leading causes of premature skin aging, often referred to as photoaging. UV radiation damages the skin’s collagen and elastin fibers, leading to wrinkles, pigmentation, and a leathery skin texture.
Smoking
The harmful toxins in cigarette smoke significantly speed up the aging process. Smoking narrows the blood vessels in the skin, impeding blood flow and leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients. This results in wrinkles, a dull complexion, and a variety of other skin issues.
Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption dehydrates the skin, which can lead to dryness, puffiness, and eventually wrinkles. Alcohol can also lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which accelerate the aging process.
Stress
Chronic stress can have profound effects on the skin, accelerating aging by promoting inflammation and impairing the skin’s ability to repair itself. This can lead to premature wrinkles, dullness, and other signs of aging.
Poor Nutrition
A diet lacking in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can accelerate skin aging. These nutrients are necessary for the skin to regenerate and repair itself. Without them, the skin can become dry, dull, and more prone to wrinkles and other signs of aging.
Pollution
Airborne pollutants can damage the skin by causing inflammation and oxidative stress. This leads to a breakdown of collagen and elastin, causing wrinkles, age spots, and other signs of aging.
In conclusion, understanding the role of intrinsic and extrinsic factors in skin aging is critical in the field of dermatology and cosmetology. While we can’t change our genetic makeup or stop the clock, we can certainly influence extrinsic factors. Through a combination of lifestyle changes, protective measures, and possibly interventions like skin treatments, the effects of these aging factors can be mitigated, promoting healthier, younger-looking skin.






