Exploring the Complexity of Organs and Body Systems: Function and Interconnectivity
The human body is a remarkable masterpiece of organization and integration, consisting of organs and body systems that work harmoniously to sustain life and ensure optimal functioning. This article delves into the intricate nature of organs and body systems, highlighting their specialized functions and the collaborative efforts they undertake to maintain overall health.
Organs and Body Systems
Organs
Specialized Tissues Working in Unison Organs are composed of specialized tissues that collaborate to perform specific functions essential for the body’s survival and well-being. Each organ has a distinct structure and performs unique tasks. Here are some notable examples:
- Brain: The brain, the command center of the nervous system, controls and coordinates bodily functions, cognition, and emotions.
- Heart: The heart, a muscular organ, pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body, ensuring the delivery of oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products.
- Lungs: The lungs facilitate respiration by extracting oxygen from the air and eliminating carbon dioxide, playing a crucial role in the exchange of gases.
- Stomach and Intestines: These digestive organs process food, breaking it down into nutrients and absorbing them into the bloodstream to nourish the body.
- Liver: The liver is responsible for detoxification, bile production, metabolism, and the storage of essential nutrients.
- Kidneys: The kidneys filter blood, eliminating waste products and excess fluids to maintain fluid balance and regulate blood pressure.
- Eyes: The eyes allow vision, enabling us to perceive and interpret the world around us.
- Skin: The skin, the largest organ of the body, acts as a protective barrier, regulates body temperature, and facilitates sensory perception.
Body Systems
Collaboration for Optimal Functioning Body systems, also known as organ systems, are groups of organs that work together to perform specific functions vital for the body’s overall well-being. Each system has a unique set of functions and often relies on the seamless cooperation of multiple organs. Let’s explore some essential body systems:
- Nervous System: The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, coordinating and regulating bodily activities, enabling sensory perception, and facilitating communication.
- Cardiovascular System: Comprised of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, the cardiovascular system transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells throughout the body.
- Respiratory System: The respiratory system, comprising the lungs, airways, and respiratory muscles, facilitates the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the body and the external environment.
- Digestive System: The digestive system, including the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas, processes food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste products.
- Urinary System: The urinary system, composed of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, removes waste products from the blood, maintains fluid balance, and regulates electrolyte levels.
- Musculoskeletal System: The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, muscles, joints, and connective tissues, providing support, protection, and enabling movement and locomotion.
- Integumentary System: The integumentary system, primarily comprising the skin, hair, and nails, offers protection, regulates body temperature, and facilitates sensation.
Body Systems, Their Functions, and Major Organs | |||
Body Systems | Function | Major Organs and Related Structures | Why Know This? |
Circulatory  | Controls blood movement throughout the body | Heart, blood vessels | Massage affects the circulatory system, and good blood flow affects hair growth. Facial services and shaving (if permitted) benefit from awareness of arteries and veins for safety. |
Digestive  | Breaks food down into nutrients or waste for nutrition or excretion | Stomach, intestines, | Good nutrition allows optimum functioning of all body systems |
Endocrine  | Controls hormone levels within the body that determine growth, development, reproduction, and health of entire body | Endocrine glands, hormones | Hormones produced by the endocrine system directly impact hair and skin. Some skin and hair conditions are a result of hormones. |
Excretory  | Eliminates waste from the body, reducing the buildup of toxins | Kidneys, liver, skin, large intestine, lungs | The excretory system eliminates toxic substances that can affect other body system functions. |
Immune (lymphatic)  | Protects the body from disease by developing immunities and destroying pathogens and toxins | Lymph, lymph nodes, lymph vessels, spleen | The immune system protects the body from illness. Massage affects the lymphatic system. |
Integumentary 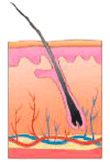 | Provides a protective covering and regulates body temperature | Skin, oil glands, sweat glands, hair, nails | The skin is the body’s largest organ and its first line of defense against illness. Cosmetology services are directly affected by the health of the integumentary system. |
Muscular  | Covers, shapes, and holds the skeletal system in place; muscles contract to allow for movement of body structures | Muscles | Massage performed during cosmetology services affects the |
Nervous  | Coordinates all other body systems, allowing them to work efficiently and react to the environment | Brain, spinal cord, nerves, eyes | To provide safe and effective facial and nail services, cosmetologists need an understanding of the nervous system. |
Reproductive  | Produces offspring and differentiates males from females as assigned at birth | Uterus, ovaries, penis, testes | The reproductive system and hormonal changes that occur with different life stages affect hair growth, hair loss, and the skin. |
Respiratory  | Makes blood and oxygen available to body structures through respiration; eliminates carbon dioxide | Lungs, air passages | Adequate oxygenation of tissues allows optimum cell functioning; infection can be spread through respiration, affecting safety and cleanliness. |
Skeletal  | Forms the physical foundation of the body; composed of 206 bones connected by moveable and immovable joints | Bones, joints | Important for protecting your own body mechanics when working, as well as knowing bone structure when providing treatments, including makeup applications. |
Body Systems, Their Functions, and Major Organs
The human body is a complex and interconnected network of organs and body systems that collaboratively contribute to its overall function and well-being. Each organ, with its unique structure and function, plays a crucial role in supporting life. Simultaneously, body systems synergistically interact, ensuring the smooth operation of various physiological processes. Understanding the interplay between organs and body systems helps us appreciate the intricacy of the human body and underscores the significance of maintaining their health and proper functioning. By nurturing and supporting our organs and body systems through healthy lifestyle choices and medical interventions when necessary, we can optimize our well-being and live vibrant, fulfilling lives.











