Sun Damage: The Silent Accelerator of Skin Aging
The quest for a sun-kissed glow may often seem appealing, but the harsh reality is that unprotected exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) light accelerates skin aging significantly. UV light, a form of radiation, is one of the most impactful extrinsic factors that contribute to skin aging. In fact, it is estimated that approximately 80 to 85 percent of visible signs of skin aging are caused by the accumulated effects of exposure to the sun’s damaging rays. As such, understanding the impacts of UV radiation and adopting appropriate preventative measures are crucial in maintaining healthy, youthful-looking skin.

Skin Aging
The Effects of UV Radiation on the Skin
Our skin, being the body’s outermost protective layer, is exposed to various environmental factors daily, with sunlight being one of the most pervasive. UV light, a component of sunlight, is a powerful form of radiation that has a profound impact on skin health and appearance.
UV radiation primarily affects two critical proteins in our skin: collagen and elastin. These proteins are the scaffolding of our skin, providing it with firmness and elasticity. As we age, collagen and elastin naturally degrade, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. However, exposure to UV light speeds up this process significantly, leading to premature aging, or “photoaging,” characterized by symptoms like wrinkles, fine lines, hyperpigmentation, and reduced skin elasticity.
The UV light from the sun comes in two forms: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, damaging collagen and elastin fibers. UVB rays, on the other hand, are responsible for sunburns, damaging the skin’s outermost layers. Both types of UV light contribute to skin aging and increase the risk of skin cancer.
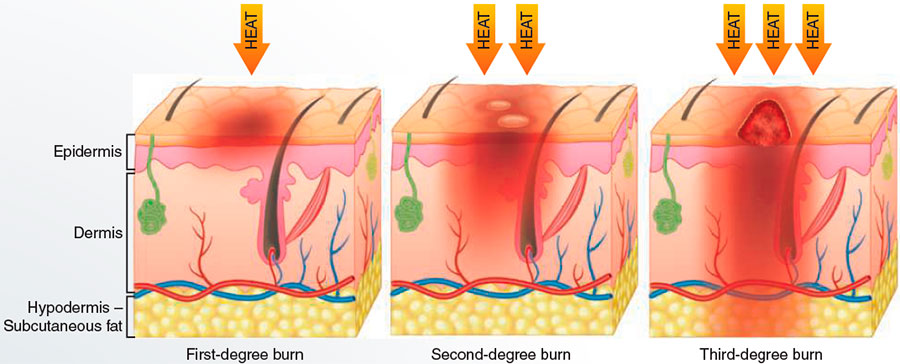
The Dangers of Sunburn
While a sunburn might seem like a temporary inconvenience, its implications go far beyond red, peeling skin. Sunburn is an acute inflammatory response to excessive UV radiation. It can lead to direct DNA damage in the skin cells, triggering mutations that can ultimately lead to skin cancer. Severe sunburns can even cause second-degree burns, characterized by blistering and possible skin damage that extends beyond the outermost layer of the skin.
Protecting the Skin from Sun Damage
Given the considerable impact of UV radiation on skin health and appearance, implementing a comprehensive sun protection strategy is essential. Here are a few ways to protect your skin from sun damage:
- Apply Sunscreen Daily: Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays is crucial. A sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher should be applied every day, even on cloudy days, as up to 80% of UV radiation can pass through clouds.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Clothing can be an effective barrier against UV rays. Wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved garments can provide additional protection.
- Seek Shade: Whenever possible, seek shade, especially during the sun’s peak intensity hours (typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.).
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation and pose a similar risk to natural sunlight. It’s best to avoid them altogether.
Understanding the harmful effects of sun exposure and implementing protective measures can significantly decelerate skin aging and reduce the risk of skin cancer. Therefore, it’s never too late to start protecting your skin from the sun’s damaging rays, preserving your skin’s health and youthful appearance for years to come.






