Understanding Skin Pigments: A Comprehensive Guide for the Skincare Specialist
Skin pigmentation plays a crucial role in our appearance, health, and ethnicity. It significantly influences our perceived beauty, skin aging, and susceptibility to skin conditions and disorders. As skincare specialists, it is essential to understand the nature of skin pigments and their underlying mechanisms to provide the best skincare advice and treatments.

Skin Pigments
What are Skin Pigments?
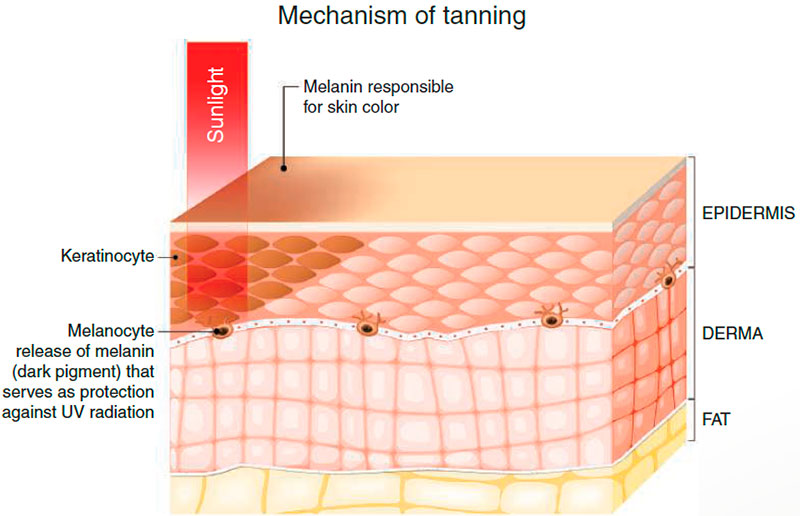
The color of our skin, whether fair, medium, or dark, primarily depends on melanin – minute grains of pigment produced by specialized cells known as melanocytes. These cells deposit melanin into the cells of the stratum germinativum (the deepest layer of the epidermis) and the papillary layers of the dermis.
Interestingly, all individuals, regardless of skin color, possess approximately the same number of melanocytes. However, the amount of melanin these cells produce varies significantly among individuals. The size, quantity, and makeup of the melanin granules determine the depth and tone of an individual’s skin, hair, and eye color.
Internal and External Factors Influencing Melanin Production
Melanin production and activation are influenced by both internal and external factors.
- Internal Factors: Genetic differences play a critical role in skin color. Individuals with darker skin usually have more active melanocytes, leading to higher melanin production.
- External Factors: One of the most impactful external factors is sun exposure. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun stimulates melanin production, which, in turn, protects the underlying skin cells by absorbing and blocking UV radiation. However, melanin alone cannot provide complete protection against UV-induced skin damage. It is why daily use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 15 or higher is highly recommended to prevent sunburn, skin cancer, and premature aging.
Types of Melanin
The human body synthesizes two types of melanin:
- Pheomelanin: This pigment ranges in color from red to yellow. Individuals dominant in pheomelanin often exhibit rosy skin with red or neutral hair tones.
- Eumelanin: Eumelanin pigment is dark brown to black. People dominant in eumelanin generally have cooler hair and skin tones.
It’s common for individuals to have a mix of both pigment types, resulting in golden skin and hair tones.
Implications for Skincare Specialists
Understanding skin pigmentation is vital for skincare specialists as it directly impacts treatment plans, product recommendations, and skincare advice.
- Treatment Plans: Certain procedures, such as chemical peels or laser treatments, may have different effects depending on a person’s melanin levels. For example, darker skin types, due to higher melanin levels, are more prone to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Therefore, skincare specialists need to adjust treatment protocols accordingly.
- Product Recommendations: Knowing an individual’s skin pigment type can guide the selection of skincare products. For instance, individuals with darker skin or those with higher melanin production may require skincare products with higher SPF.
- Skincare Advice: Advice on sun protection, skincare routines, and lifestyle habits can be tailored based on the individual’s skin pigmentation.
In conclusion, understanding skin pigmentation can significantly enhance a skincare specialist’s ability to provide personalized care. As we continue to embrace the diversity of human skin tones, a deep understanding of skin pigments becomes all the more important.






